ACUPCC Progress from Greenhouse Gas Reporting Trends
 by Ashka Naik, Director of ACUPCC Initiatives, Second Nature
by Ashka Naik, Director of ACUPCC Initiatives, Second Nature
As of November 2013, 616 signatory institutions have submitted 1998 GHG Inventories in total.
616 institutions have submitted at least one GHG report. 492 institutions have submitted at least two GHG reports, with which we have datasets to analyze trends of emission within the ACUPCC network.
Figure 1: The following figure highlights the breakdown of how many GHG reports have been submitted by signatory institutions.
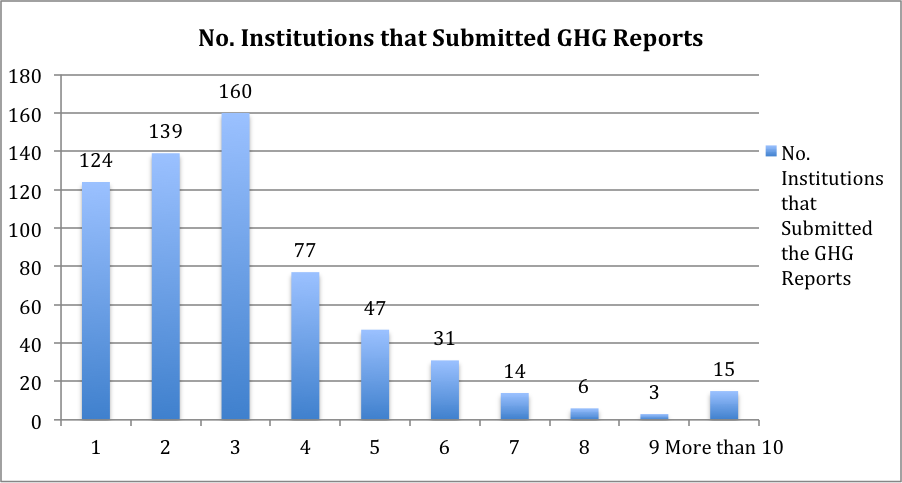
The 492 institutions that have submitted at least two GHG reports present the following trends on their GHG emissions.
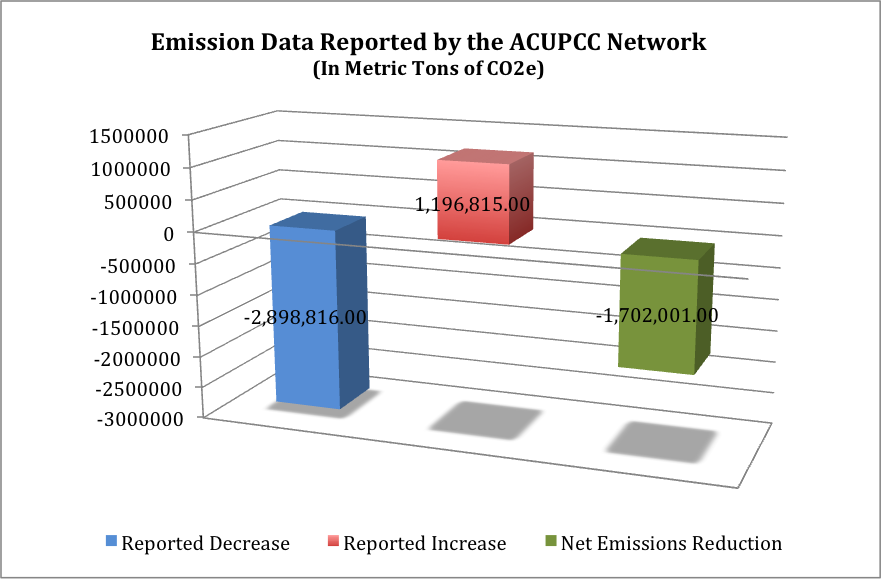
- 286 (58%) of the 492 signatory institutions show a reduction totaling 2,898,816 metric tons of CO2e.
- 198 (40%) of the 492 signatory institutions show an increase of 1,196,815 metric tons of CO2e.
- 8 of the 492 signatory institutions show no change in their emissions.
- The cumulative emissions reduction from these 492 signatory institutions is 1,702,001 metric tons of CO2e.
Figure 2: The following figure highlights the net emissions reduction (in metric tons of CO2e) by the 492 signatory institutions that have submitted two or more GHG reports.
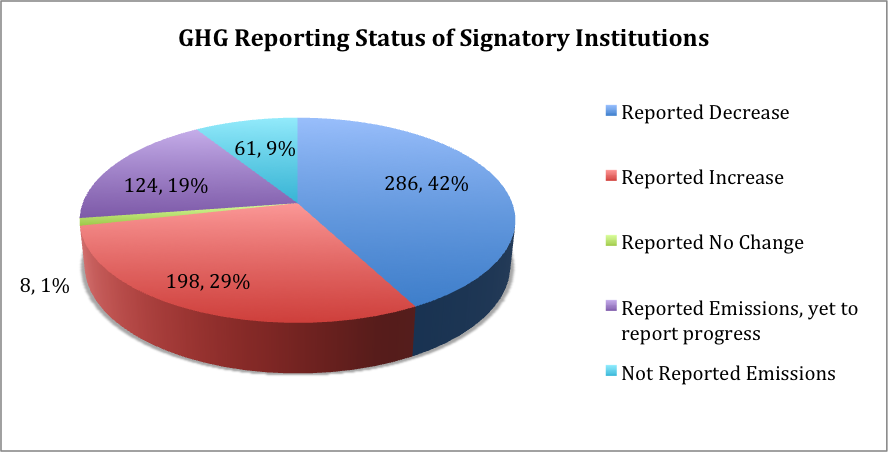
This means that 42% of the ACUPCC network has reported their ACUPCC implementation activities have resulted in emission reductions. 29% have reported increase, and 1% has reported no change in their emission. 18% have reported on their baseline emission, however, have not reported the progress (as they have submitted only one GHG report) and 9% of the signatory institutions have not reported their baseline emissions (these institutions may not have a GHG report due yet or may have missed their deadline), as of November 2013.
Figure 3: The following figure highlights the percentage of the ACUPCC network that has reported on different trends of GHG emissions.
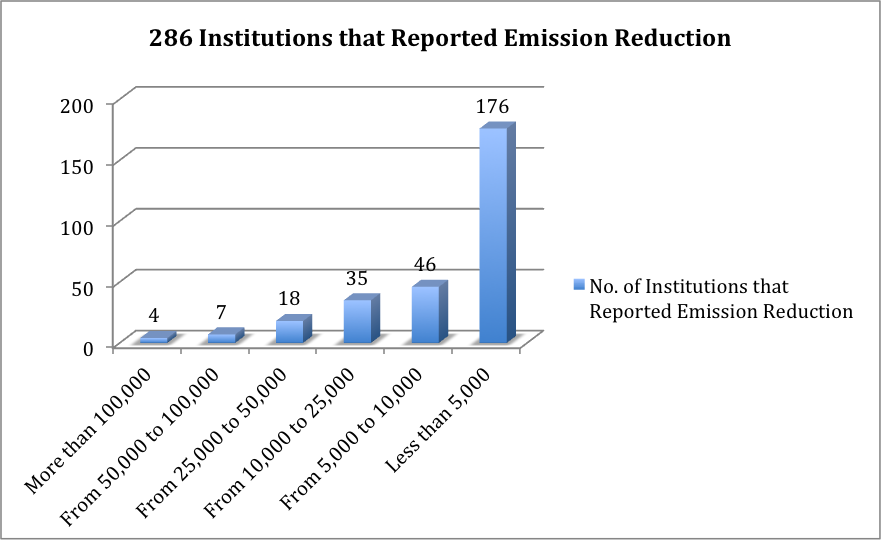
Out of the 286 signatory institutions that reported emission reduction, 176 (61.5%) reported reduction of less than 5,000 Metric Tons of CO2e. Out of the 286, 1.3% reported reduction of more than 100,000 Metric Tons of CO2e.
Figure 4: The following figure represents further breakdown of the 286 signatory institutions that reported emission reductions.
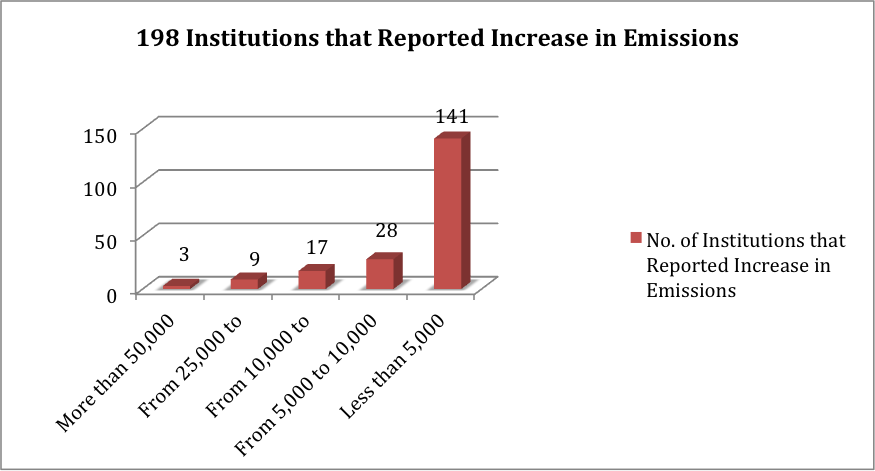
Out of the 198 signatory institutions that reported increase in their operational emissions, 141 (71.2%) reported increase of less than 5,000 Metric Tons of CO2e. Out of the 198, 1.5% reported increase of more than 100,000 Metric Tons of CO2e.
Figure 5: The following figure represents further breakdown of the 198 signatory institutions that reported increase in their operational emissions.
All in all, these charts demonstrate that the ACUPCC implementation activities on campus are translating into net reductions for the network. As more institutions start reporting on their progress, we will have access to wider datasets to further underscore the trend highlighted in the above analysis.
Based on the net reduction of 1,702,001 metric tons of CO2eby the ACUPCC network, using the EPA Equivalencies Calculator, we can say that the mitigated emissions are equivalent to:
- Annual greenhouse gas emissions from 354,584 passenger vehicles, or
- CO2 emissions from 190,807,287 gallons of gasoline consumed, or
- CO2 emissions from 22,448 tanker trucks’ worth of gasoline, or
- CO2 emissions from the electricity use of 234,177 homes for one year, or
- Carbon sequestered by 43,641,051 tree seedlings grown for 10 years, or
- Greenhouse gas emissions avoided by recycling 637,454 tons of waste instead of sending it to the landfill.
[NOTE: The ACUPCC is not responsible for the accuracy or validity of the data submitted by signatory institutions. The ACUPCC does not require institutions to verify GHG emissions or any other information submitted in their reports. However, it does encourage and trust institutions to submit the most accurate data available and to be transparent about their data collection processes.]
